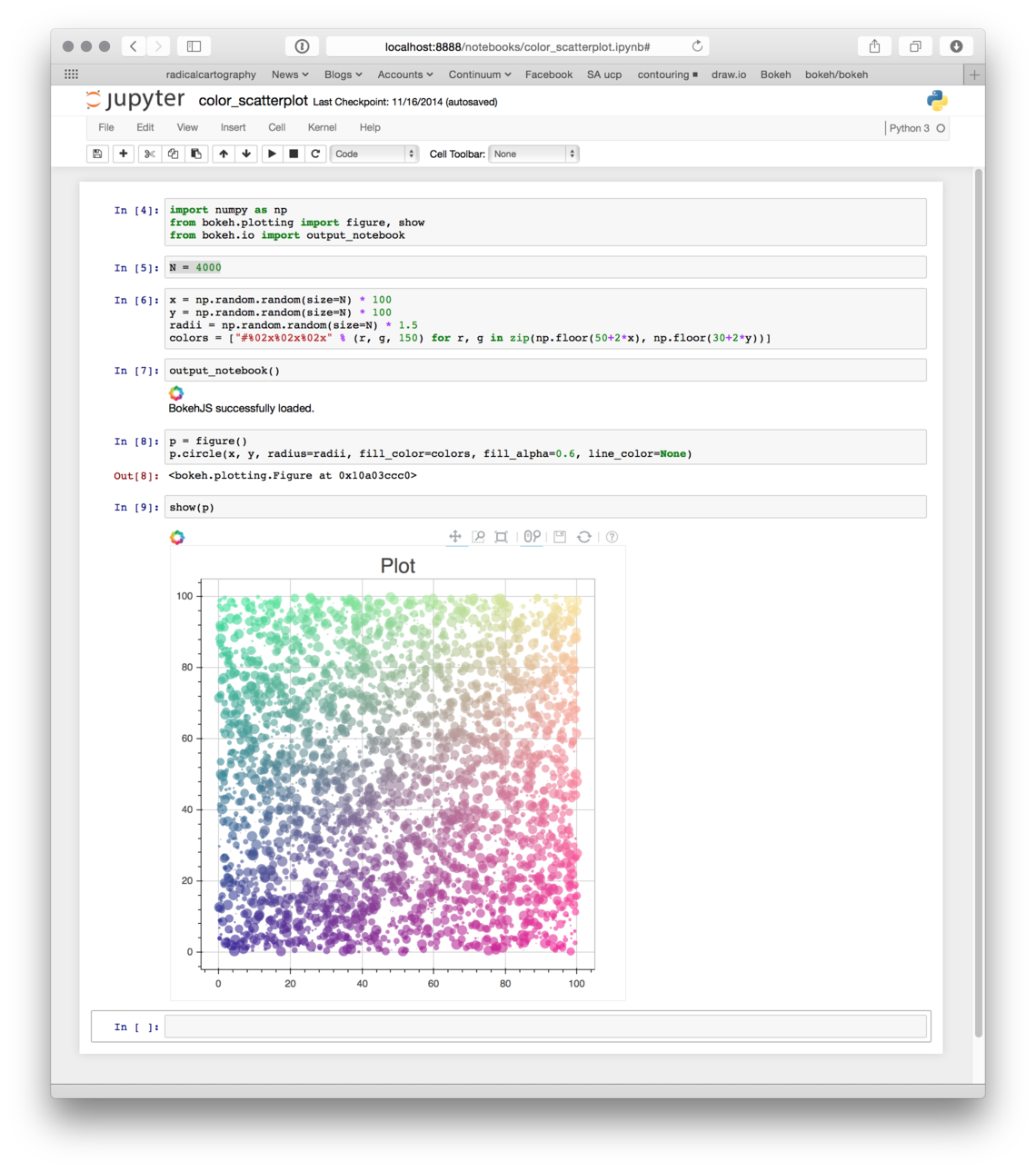
Working in the Notebook¶
Inline Plots¶
To display Bokeh plots inline in an Jupyter/Zeppelin notebook, use the
output_notebook() function from bokeh.io instead of (or in addition to)
the output_file() function we have seen previously. No other modifications
are required. When show() is called, the plot will be displayed inline in
the next notebook output cell. You can see a Jupyter screenshot below:
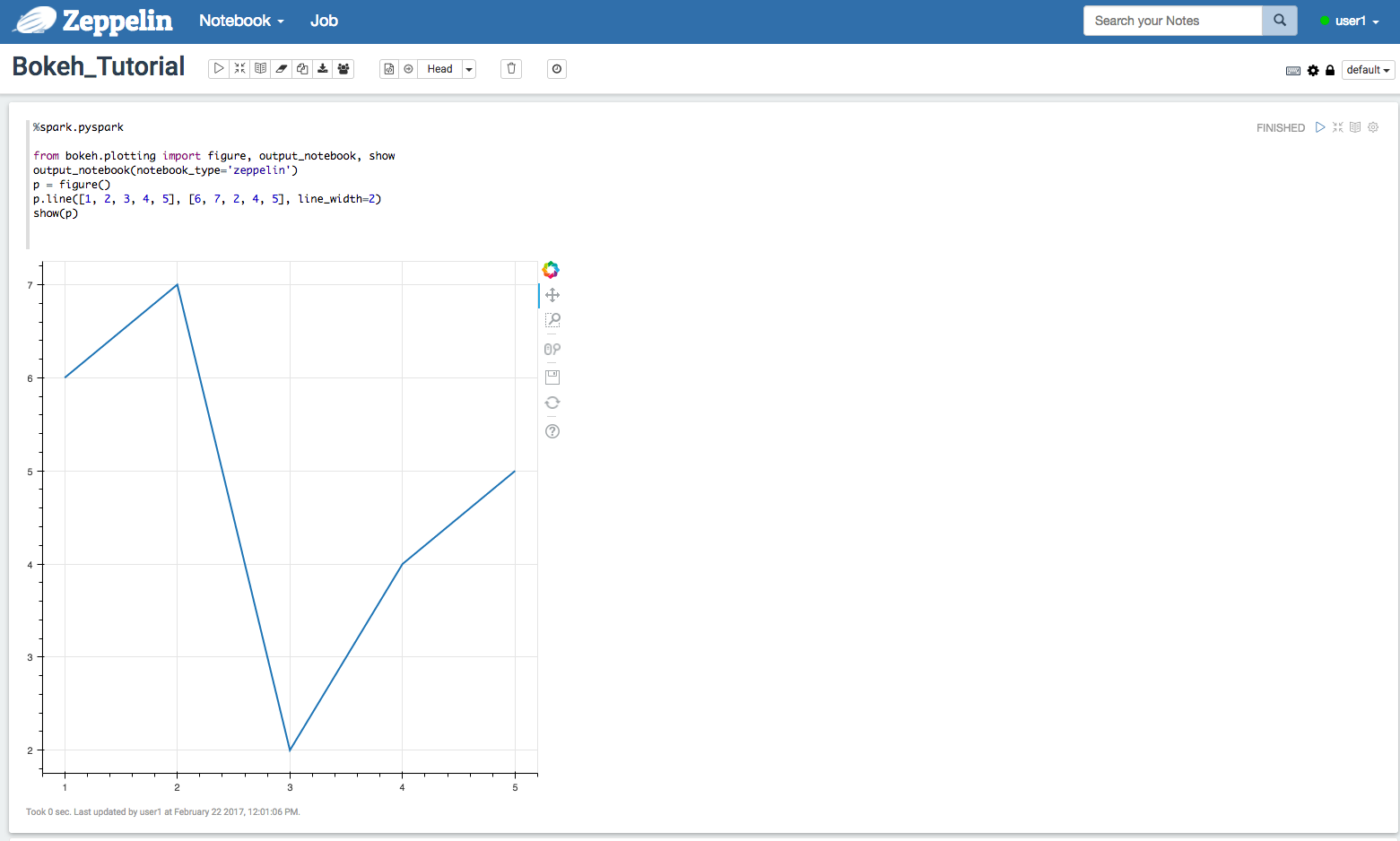
By defaults, output_notebook() apply to Juypter. If you want to use bokeh
to display inline plots in Zeppelin, you need to specify notebook_type
to zeppelin in output_notebook(). Here’s one Zeppelin screenshot.
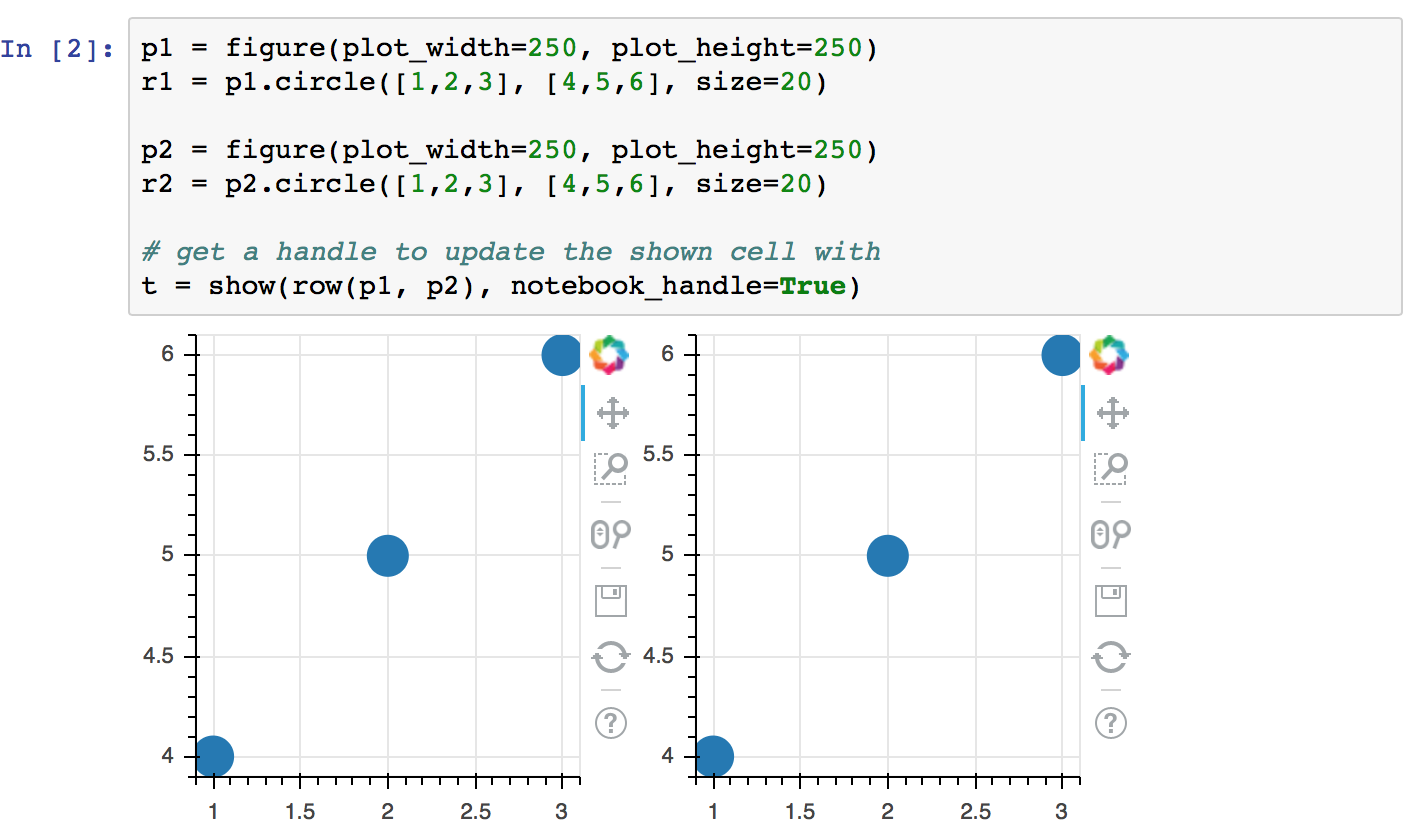
Notebook Handles¶
It is possible to update a previously shown plot in-place. When the argument
notebook_handle=True is passed to show() then a handle object is returned.
This handle object can be used with the push_notebook() function to update
the plot with any recent changes to plots properties, data source values, etc.
But notebook handle is only supported in Jupyter, not supported by Zeppelin yet.
The following screenshots walk through the basic usage of notebook handles.
- First, import standard functions, as well as
push_notebook():

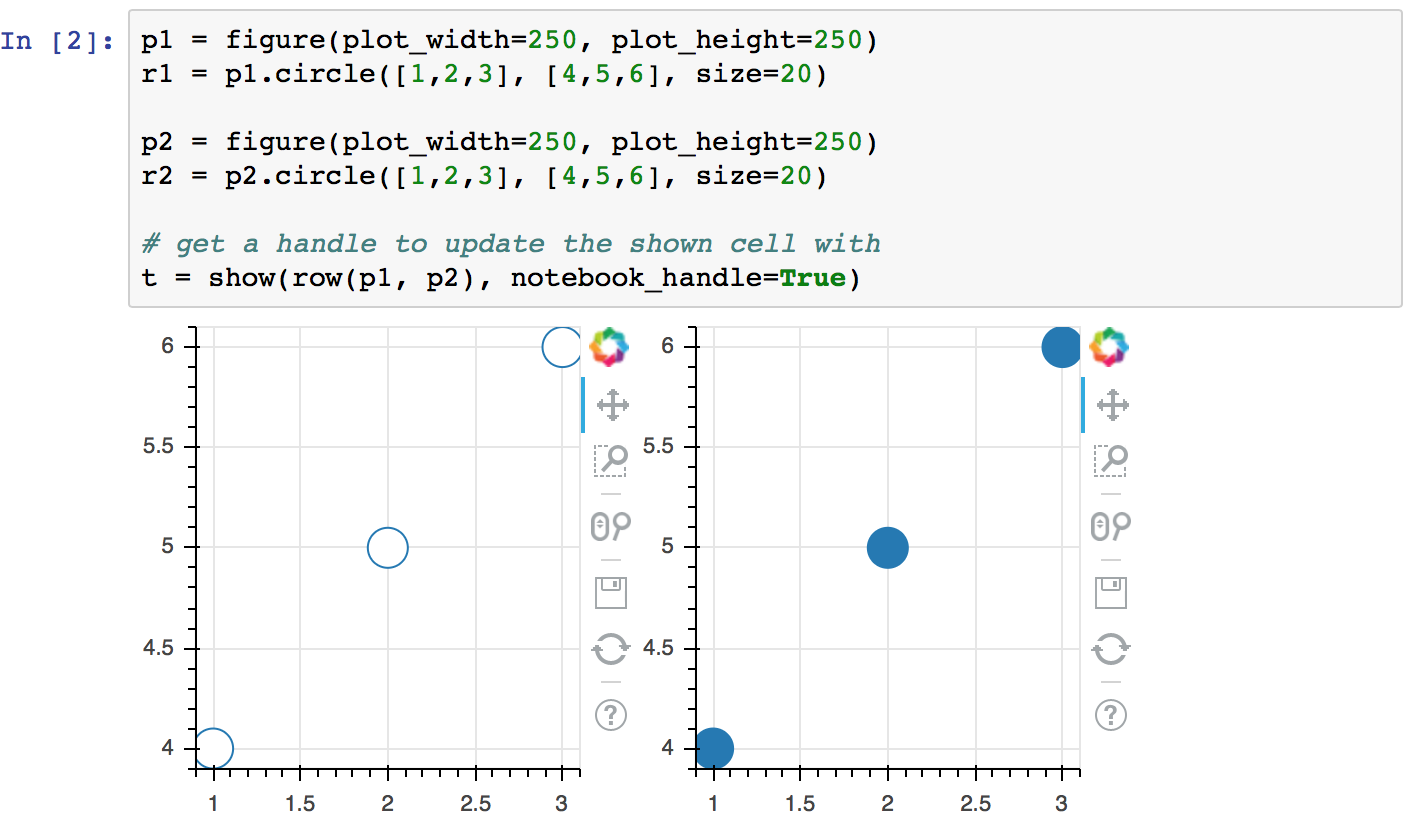
- Next, create some plots, and make sure to pass
notebook_handle=Truetoshow():
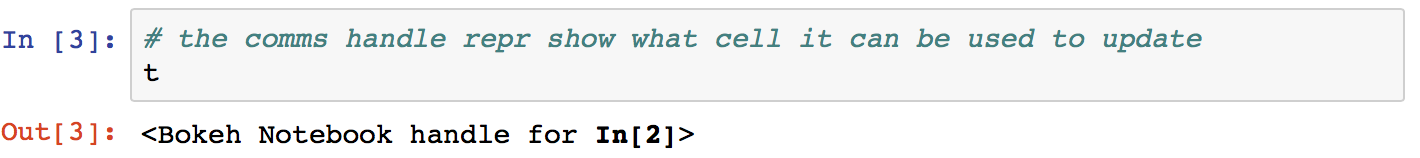
- Looking at the handle, see that it is associated with the output cell
for
In[2]that was just displayed:
- Now, update any properties of the plot, then call
push_notebook()with the handle:

- After doing so, note that the earlier output cell for
In[2]has changed (without being re-executed)
More detailed demonstrations of using notebook handles can be found in the following example notebooks:
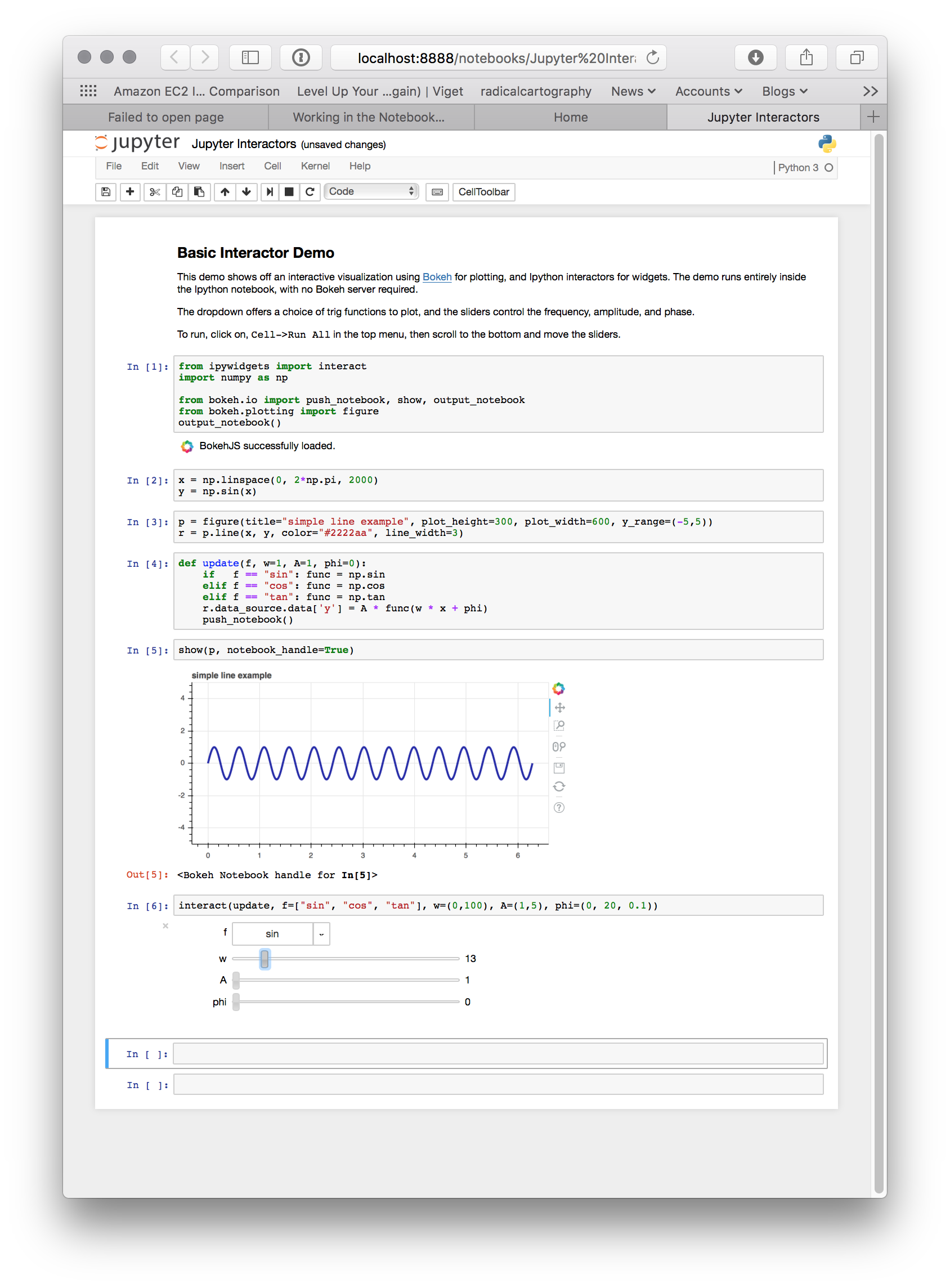
Jupyter Interactors¶
It is possible to drive updates to Bokeh plots using Jupyter notebook widgets,
known as interactors. The key doing this is the push_notebook() function
described above. Typically it is called in the update callback for the
interactors, to update the plot from widget values. A screenshot of the
examples/howto/notebook_comms/Jupyter Interactors.ipynb example
notebook is shown below: