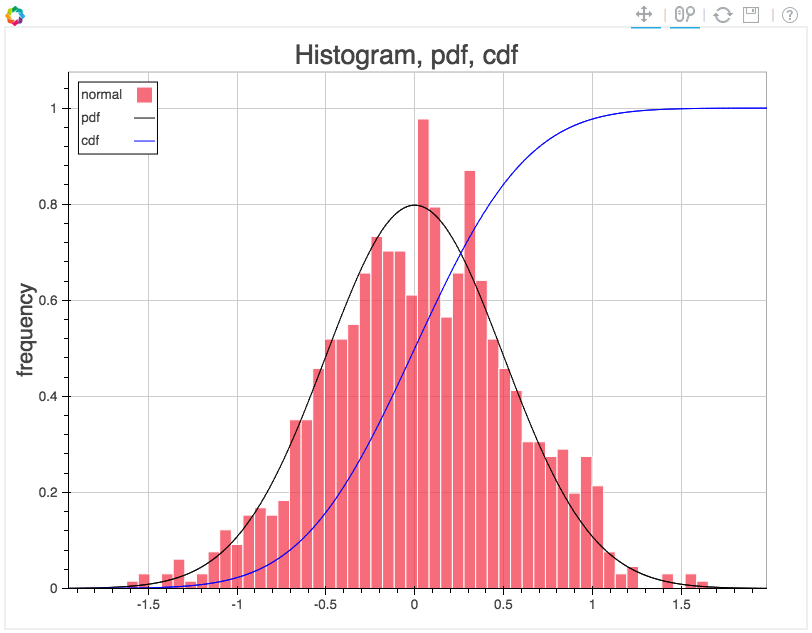
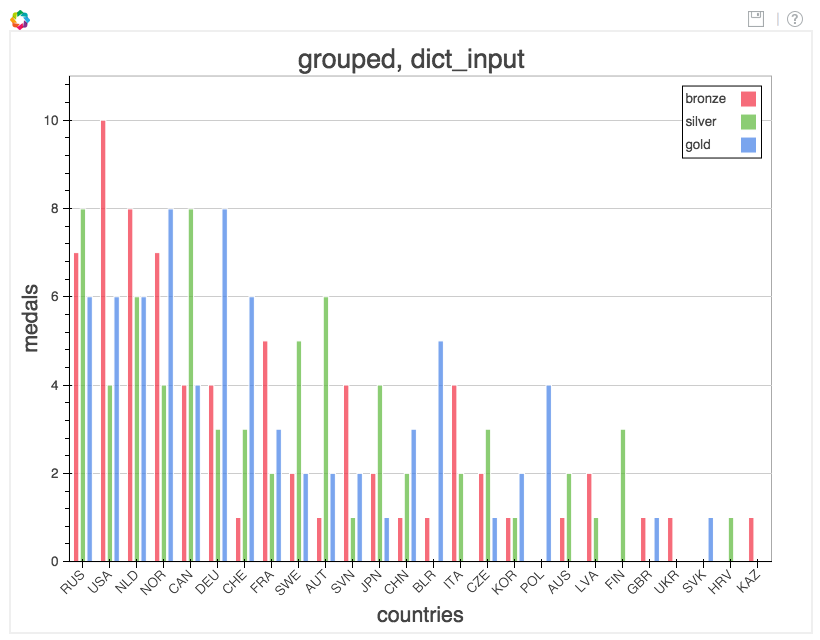
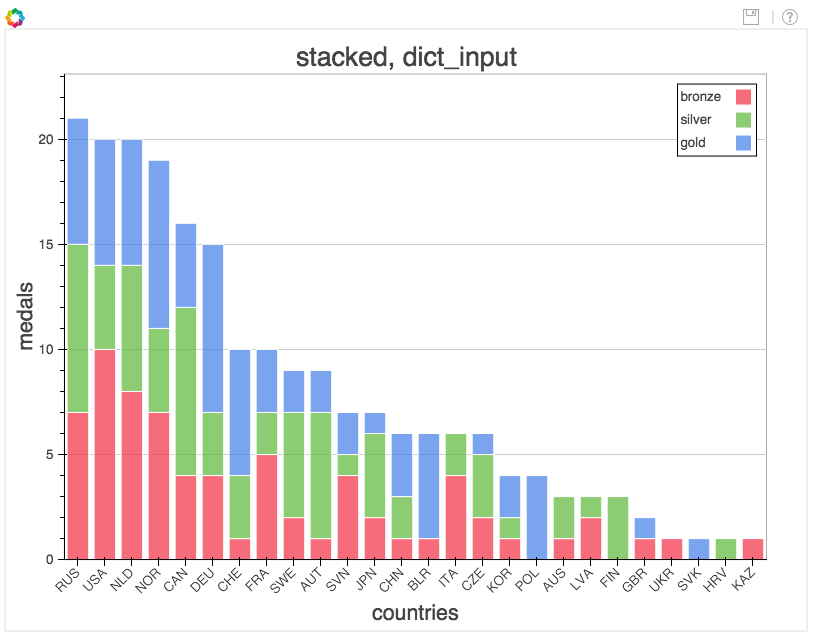
from collections import OrderedDict
from bokeh.charts import Area, show, output_file
# create some example data
xyvalues = OrderedDict(
python=[2, 3, 7, 5, 26, 221, 44, 233, 254, 265, 266, 267, 120, 111],
pypy=[12, 33, 47, 15, 126, 121, 144, 233, 254, 225, 226, 267, 110, 130],
jython=[22, 43, 10, 25, 26, 101, 114, 203, 194, 215, 201, 227, 139, 160],
)
output_file(filename="area.html")
area = Area(
xyvalues, title="Area Chart",
xlabel='time', ylabel='memory',
stacked=True, legend="top_left"
).legend("top_left")
show(area)